Automated cascade design
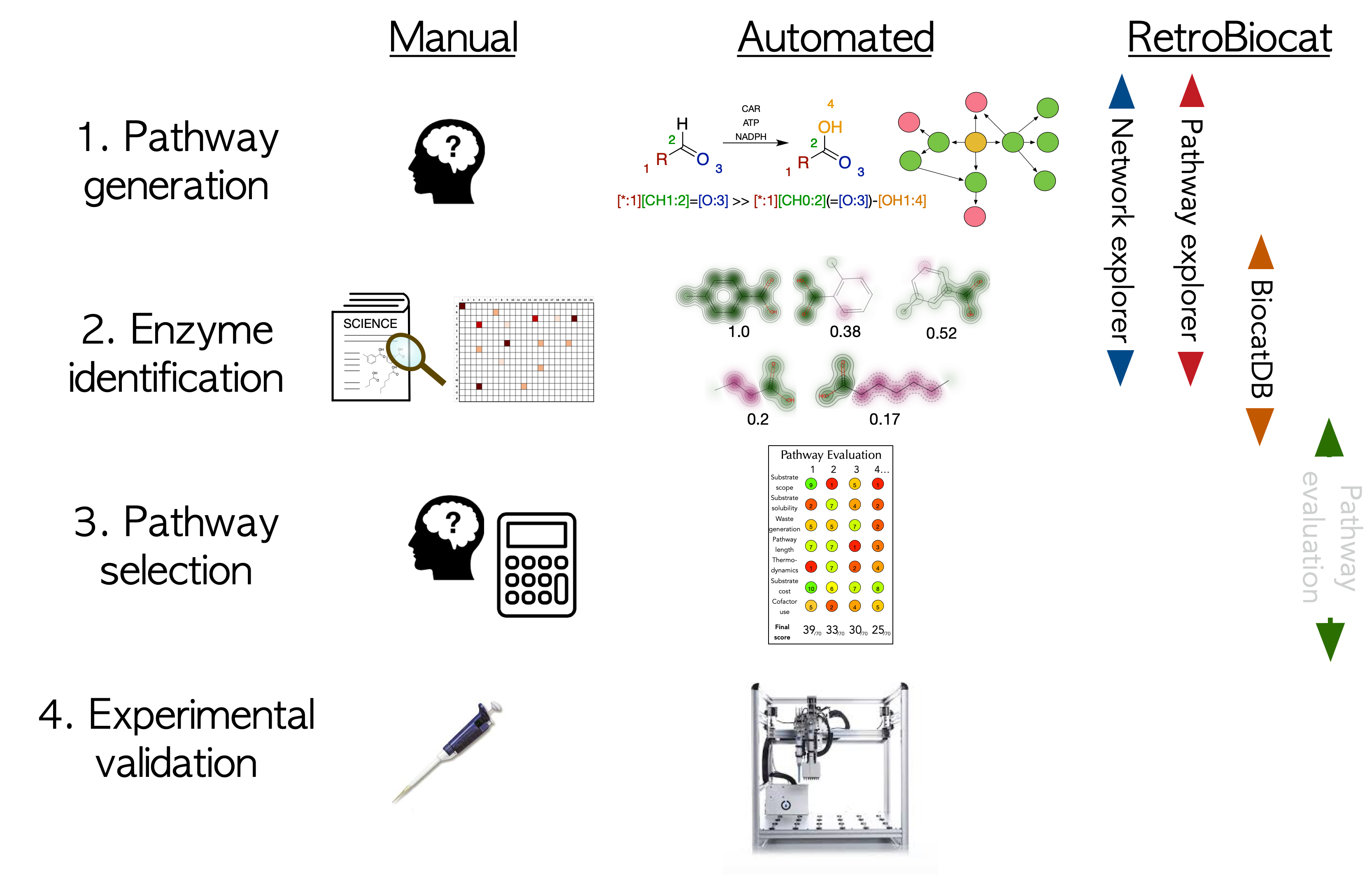
Broadly, the design of a biocatalytic route to a target molecule can be split into four steps.
Step 1
Step 1 requires biocatalytic retrosynthesis to be employed to work backwards from a target molecule to a suitable starting material. Manually this relies on expert knowledge of what biotransformations are possible. Alternatively, reaction rules can be programmed or extracted from available reaction information and applied iteratively for automated retrosynthesis towards a suitable starting material.
Step 2
With a number of potential pathways in hand, step 2 requires specific enzymes to be selected to carry out each enzymatic step. In many cases there are a great many potential sequences which could theoretically complete it. Researchers manually selecting enzymes will typically rely on literature searches, or more recently enzyme screening panels, to identify suitable enzymes. For a more automated approach, a database of known biotransformations can be searched for similar substrates which have been tested previously, using molecular similarity.
Step 3-4
Often a number of potential pathways are identified. Further evaluation of these pathways in step 3 can provide data-driven analysis of which are the best pathways to take forwards for experimental validation in step 4. This requires the calculation of a number of metrics such as substrate availability, enzyme selectivity, thermodynamics, cofactor usage, substrate solubility ect..
RetroBiocat
RetroBiocat seeks to offer automated solutions for steps 1-3. Network explorer offers human-led exploration of a network of possible biotransformations, with the option to add custom transformations not currently included in the program (for example chemical transformations). Pathway explorer offers automated pathway generation, with selection based on the weighted average a number available of metrics. These pathways can then be explored one at a time. Both network and pathway explorer identify specific enzymes to complete each step, where data is available.
For a more detailed look at the enzymes available for a particular biotransformation, BiocatDB offers a search portal for investigating substrate specificity for a particular enzyme or reaction.
In a future release we hope to also offer a tool for automated pathway evaluation (step 3), with integration into a complete work flow.